Repeater Insertion Model
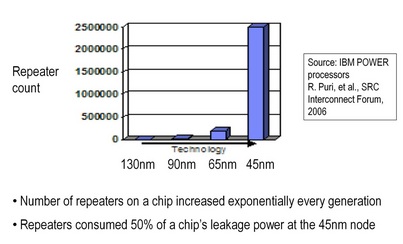
Fig. M6 shows data from IBM's POWER processors. This indicates the number of repeaters increases exponentially with scaling, and that repeaters now form a big fraction of chip power. It is therefore critical to have an energy-efficient repeater insertion model.
Figure M6: Repeater trends in IBM POWER processors.
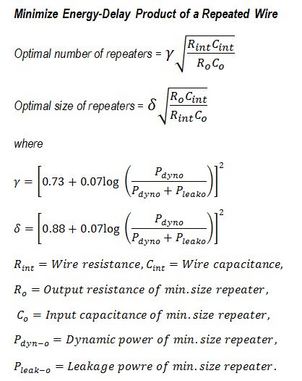
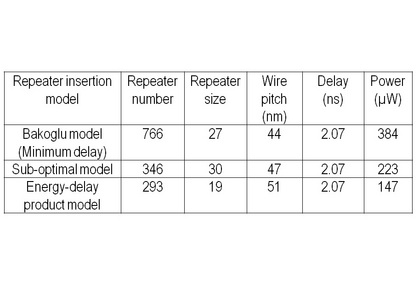
The repeater insertion model used in IntSim v2.0 is shown in Fig. M7. It minimizes energy-delay product of a repeated wire. It's derivation is shown in [22]. A comparison of this energy-delay product based model with other models in the literature [23][24] is shown in Fig. M8. It can be observed that IntSim's energy-delay product model gives the best trade-off between power, delay and area.
Fig. M7: Repeater insertion model used in IntSim v2 [22]. Fig. M8: Comparison of IntSim's repeater insertion model vs. literature [22].